

Exposure to airborne dust is generally accompanied by irritation of exposed skin, eyes, and mucous membranes.Įmergency Life-Support Procedures: Acute exposure to arsenic pentoxide exposure may require decontamination and life support for the victims.
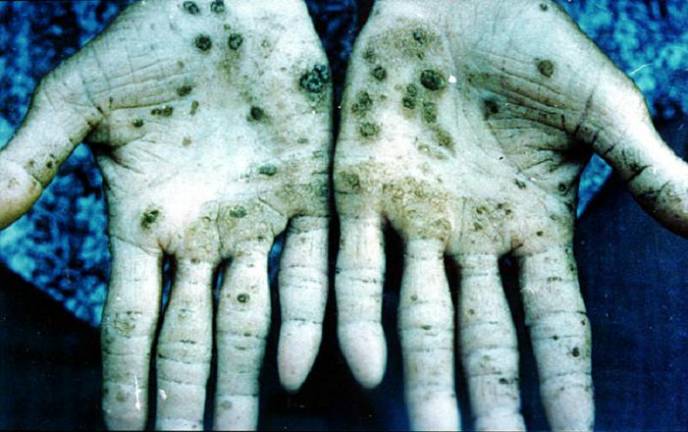
Altered mental status, seizures, and delirium are further complications of arsenic pentoxide exposure. Cardiovascular effects include shock, tachycardia (rapid heart rate), ventricular fibrillation, and other cardiac abnormalities. Garlic odor of breath and feces may be noted.

Headache, conjunctivitis (red, inflamed eyes), runny nose, and lacrimation (tearing) are also common. Signs and Symptoms of Arsenic Pentoxide Exposure: Hypotension (low blood pressure), tachycardia (rapid heart rate), dehydration, intense thirst, difficulty swallowing, vomiting, abdominal pain, and diarrhea are among the first signs and symptoms noticed following acute arsenic pentoxide exposure. Warning: Effects usually appear within 30 minutes of exposure but may be delayed for several hours. Acids often catalyze (increase the rate of) chemical reactions. Additional gas-generating reactions occur with sulfites, nitrites, thiosulfates (to give H2S and SO3), dithionites (SO2), and even carbonates: the carbon dioxide gas from the last is nontoxic but the heat and spattering from the reaction can be troublesome. Flammable and/or toxic gases are also often generated by their reactions with dithiocarbamates, isocyanates, mercaptans, nitrides, nitriles, sulfides, and weak or strong reducing agents. Their reactions with cyanide salts and compounds release gaseous hydrogen cyanide. Like other acids, materials in this group can initiate polymerization in certain classes of organic compounds. They can react with active metals, including iron and aluminum, and also many less active metals, to dissolve the metal and liberate hydrogen and/or toxic gases. but that ability varies (for example, from high for nitric acid to low for sulfuric acid and most sulfonic acids). These materials have significant ability as oxidizing agents. The resulting "bumping" spatters acid widely. The addition of water acids often generates sufficient heat in the small region of mixing to boil some of the water explosively. The dissolution of acids in water or the dilution of their concentrated solutions with water may generate significant heat.
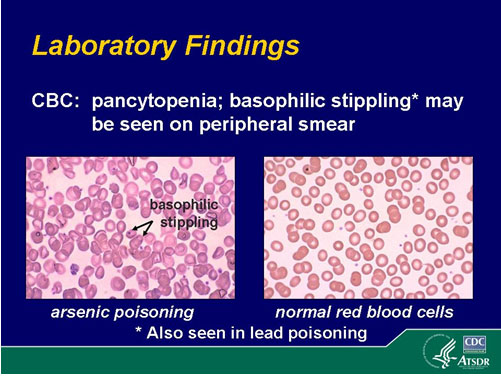
Neutralizations can generate dangerously large amounts of heat in small spaces. These neutralization reactions occur as the base accepts hydrogen ions that the acid donates. Materials in this group react with chemical bases (for example: amines and inorganic hydroxides) to form salts. The resulting solutions have pH's of less than 7.0. Oxidizing acids are generally soluble in water with the release of hydrogen ions.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
